Discover various information about How To Tell If Linear Approximation Is Over Or Under here, hopefully fulfilling your information needs.

How to Tell if Linear Approximation is Over or Under
Linear approximation is a technique used to approximate the value of a function at a given point using a straight line. It is a useful tool for simplifying complex functions and making them easier to analyze. However, it is important to be able to tell if a linear approximation is over or under, as this will affect the accuracy of the approximation.
There are two main ways to tell if a linear approximation is over or under. The first is to look at the sign of the error term. The error term is the difference between the actual value of the function and the approximate value given by the linear approximation. If the error term is positive, then the linear approximation is over. If the error term is negative, then the linear approximation is under.
The Derivative and the Error Term
The Derivative
The derivative of a function measures the rate of change of the function. If the derivative of a function is positive at a given point, then the function is increasing at that point. If the derivative of a function is negative at a given point, then the function is decreasing at that point.
The Error Term
The error term in a linear approximation is the difference between the actual value of the function and the approximate value given by the linear approximation. The error term can be positive or negative, depending on whether the linear approximation is over or under.
If the derivative of the function is positive at the point of approximation, then the function is increasing at that point. This means that the actual value of the function is greater than the approximate value given by the linear approximation. Therefore, the error term is positive and the linear approximation is over.
If the derivative of the function is negative at the point of approximation, then the function is decreasing at that point. This means that the actual value of the function is less than the approximate value given by the linear approximation. Therefore, the error term is negative and the linear approximation is under.
Tips and Expert Advice
- Use a calculator or computer program to graph the function and the linear approximation. This will help you to visualize the relationship between the two and to see if the linear approximation is over or under.
- Calculate the error term at several different points. This will give you a better idea of how the error term changes over the domain of the function.
- Use the second derivative of the function to determine the concavity of the function. If the second derivative is positive, then the function is concave up. If the second derivative is negative, then the function is concave down. This information can help you to determine if the linear approximation is over or under.
FAQ
Q: What is linear approximation?
A: Linear approximation is a technique used to approximate the value of a function at a given point using a straight line.
Q: How do I tell if a linear approximation is over or under?
A: You can tell if a linear approximation is over or under by looking at the sign of the error term. If the error term is positive, then the linear approximation is over. If the error term is negative, then the linear approximation is under.
Q: What is the error term?
A: The error term is the difference between the actual value of the function and the approximate value given by the linear approximation.
Q: How can I use the derivative to tell if a linear approximation is over or under?
A: If the derivative of the function is positive at the point of approximation, then the function is increasing at that point. This means that the actual value of the function is greater than the approximate value given by the linear approximation. Therefore, the error term is positive and the linear approximation is over.
Q: How can I use the second derivative to tell if a linear approximation is over or under?
A: If the second derivative of the function is positive, then the function is concave up. This means that the linear approximation will be under. If the second derivative is negative, then the function is concave down. This means that the linear approximation will be over.
Conclusion
Linear approximation is a useful tool for simplifying complex functions and making them easier to analyze. However, it is important to be able to tell if a linear approximation is over or under, as this will affect the accuracy of the approximation. By following the tips and advice in this article, you can improve your ability to tell if a linear approximation is over or under.
Are you interested in learning more about linear approximation? If so, please let me know in the comments below.
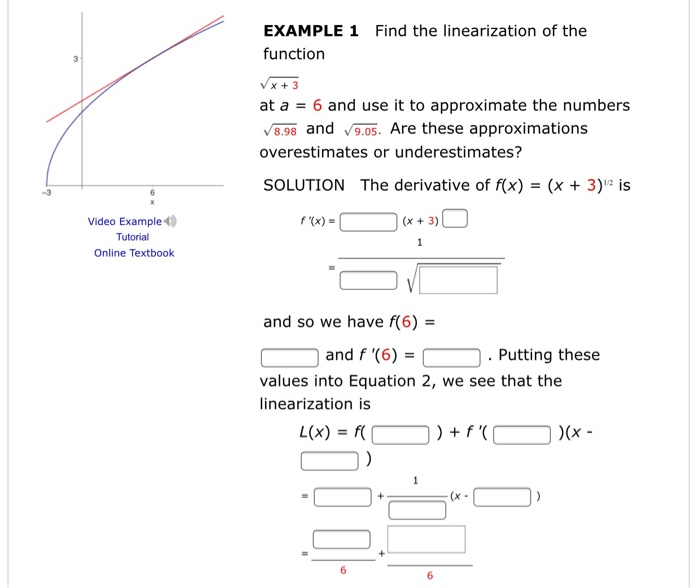
Image: www.chegg.com
You have read an article about How To Tell If Linear Approximation Is Over Or Under. Thank you for your visit, and we hope this article is beneficial for you.