Get interesting information about Rank The Alkenes From Most Stable To Least Stable, this article is specially curated for you from various reliable sources.
Ranking Alkenes from Most to Least Stable: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of organic chemistry, alkenes occupy a central role as unsaturated hydrocarbons renowned for their reactivity and diverse applications. Their stability, a crucial aspect governing their behavior, stems from the interplay of various factors, including molecular geometry, hybridization, and substitution patterns. This article embarks on a comprehensive exploration of alkenes, ranking them from most to least stable based on these fundamental principles.
Unraveling the intricacies of alkene stability requires a solid foundation in molecular structure and bonding. Alkenes, characterized by a carbon-carbon double bond, adopt a planar geometry due to sp2 hybridization of the carbon atoms involved in the double bond. This geometry optimizes overlap between atomic orbitals, resulting in a stable and rigid molecular framework.
Factors Influencing Alkene Stability
1. Degree of Substitution:
The degree of substitution, or the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon atoms of the double bond, has a profound impact on alkene stability. Alkenes with more alkyl groups, known as substituted alkenes, are generally more stable than their unsubstituted counterparts. This is attributed to the electron-donating nature of alkyl groups, which increase the electron density around the double bond and enhance its stability.
2. Hyperconjugation:
Hyperconjugation is a stabilizing effect that arises when a σ-bond interacts with an adjacent π-bond. In the case of alkenes, hyperconjugation occurs when the C-H σ-bond of an alkyl group interacts with the π-bond of the double bond. This interaction stabilizes the alkene by delocalizing electrons and reducing the overall energy of the molecule.
3. Resonance:
Resonance occurs when multiple Lewis structures can be drawn for a molecule, indicating that the electrons are delocalized over several atoms. In the case of alkenes, resonance can occur when the double bond is conjugated with a neighboring π-bond, such as a carbonyl group or another double bond. Resonance stabilizes the alkene by distributing the electron density over a larger area, reducing the overall energy of the molecule.
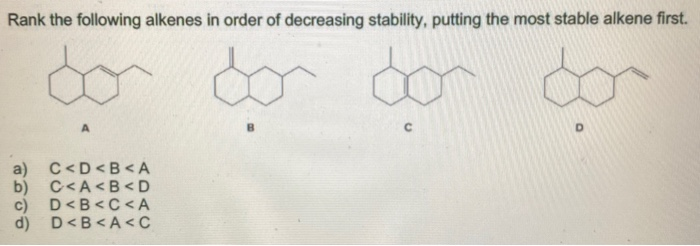
Ranking Alkenes from Most to Least Stable
Taking into account the aforementioned factors, we can now rank alkenes from most to least stable:
- Tetrasubstituted alkenes: These alkenes, with four alkyl groups attached to the double bond, are the most stable due to the maximum degree of substitution and hyperconjugation.
- Trisubstituted alkenes: With three alkyl groups attached to the double bond, these alkenes exhibit a balance between substitution and hyperconjugation, resulting in high stability.
- Disubstituted alkenes: Possessing two alkyl groups attached to the double bond, these alkenes are less stable than their tetra- and trisubstituted counterparts, but still exhibit significant stability due to substitution and hyperconjugation.
- Monosubstituted alkenes: With only one alkyl group attached to the double bond, these alkenes are less stable than the aforementioned categories due to reduced substitution and hyperconjugation.
- Unsubstituted alkenes (alkenes): These alkenes, with no alkyl groups attached to the double bond, possess the lowest stability due to the absence of substitution and hyperconjugation.
Conclusion
Understanding the stability of alkenes is paramount in predicting their reactivity and behavior. By considering factors such as substitution, hyperconjugation, and resonance, we can effectively rank alkenes from most to least stable. This knowledge empowers chemists to design, synthesize, and manipulate alkenes with desired properties, paving the way for advancements in various fields of chemistry and materials science.
We invite you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of alkenes and explore their diverse applications. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below, and let’s continue the discussion on this captivating topic.
FAQ
- What factors determine the stability of alkenes?
- The degree of substitution, hyperconjugation, and resonance.
- Which alkenes are the most stable?
- Tetrasubstituted alkenes are the most stable due to the maximum degree of substitution and hyperconjugation.
- How can I improve the stability of an alkene?
- By increasing the degree of substitution, promoting hyperconjugation, or introducing resonance.
- What are some applications of alkenes?
- Alkenes are used in the synthesis of plastics, fuels, and pharmaceuticals, among other applications.
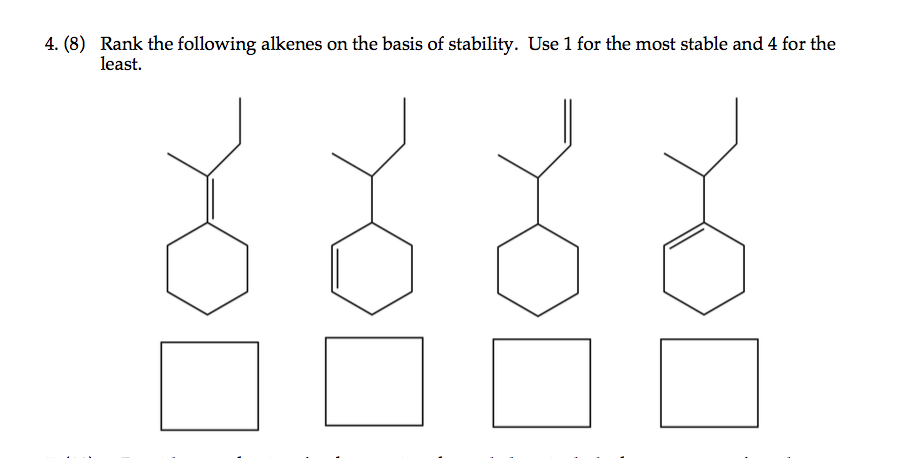
Image: www.chegg.com
You have read Rank The Alkenes From Most Stable To Least Stable on our site. Thank you for your visit, and we hope this article is beneficial for you.